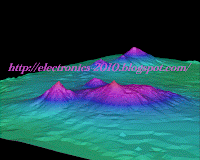
What is a digital elevation model?
Digital elevation models, or DEMs are digital representations of a region's geographical topography (ground or surface) characteristics. They are also sometimes called "digital terrain models" or DTM. However, unlike DTM, MAN offers continuous elevation data over an area of land. DTM as line cards contour and topographic maps are not considered to Because of this, MAN.
Most digital elevation models are built using remote sensing techniques and tools such as radar imaging satellite and aircraft. However, in some cases, data obtained by the traditional method of surveying is also directly implemented in the creation of numerical models. Some of the most common uses of DEMs are in the so-called digital information systems (DIS). These systems are used by governments and large industries to assess and analyze the conditions for a given region. However MNA and DIS is increasingly used in the field of consumer electronics that implement mobile bases location and technology.
Methods of creating DEMs
The tool most sophisticated and powerful mount digital elevation models is called interferometric synthetic aperture radar. It works by using radar images taken by satellites in orbit to create maps of areas 10 kilometers on each side. Two passages are all that is needed to produce such a card, which usually has a resolution of 10 meters.
Digital image correlation is another, much older and less powerful, method of production of digital elevation models. This method combines two optical images taken from an airplane or a satellite earth observation during a single pass. These two images taken from different angles, creating a set of more comprehensive data for a given geographical area. All usable raw altimetry data have been produced using this method. The satellite was used SPOT 1 in 1986.
Finally, there is the cadastre direct. This method has been used for over a hundred years and data collected by this method is still used in digital elevation models today, including the mountainous regions that are difficult to map precise using remote sensing techniques.
Current Uses
The digital elevation maps are now used in a variety of areas. Among these are services and GPS location of consumers in other basic services, flight simulators, land evaluation, precision agriculture, transportation systems and intelligent systems developed to support driver.
Digital elevation models, or DEMs are digital representations of a region's geographical topography (ground or surface) characteristics. They are also sometimes called "digital terrain models" or DTM. However, unlike DTM, MAN offers continuous elevation data over an area of land. DTM as line cards contour and topographic maps are not considered to Because of this, MAN.
Most digital elevation models are built using remote sensing techniques and tools such as radar imaging satellite and aircraft. However, in some cases, data obtained by the traditional method of surveying is also directly implemented in the creation of numerical models. Some of the most common uses of DEMs are in the so-called digital information systems (DIS). These systems are used by governments and large industries to assess and analyze the conditions for a given region. However MNA and DIS is increasingly used in the field of consumer electronics that implement mobile bases location and technology.
Methods of creating DEMs
The tool most sophisticated and powerful mount digital elevation models is called interferometric synthetic aperture radar. It works by using radar images taken by satellites in orbit to create maps of areas 10 kilometers on each side. Two passages are all that is needed to produce such a card, which usually has a resolution of 10 meters.
Digital image correlation is another, much older and less powerful, method of production of digital elevation models. This method combines two optical images taken from an airplane or a satellite earth observation during a single pass. These two images taken from different angles, creating a set of more comprehensive data for a given geographical area. All usable raw altimetry data have been produced using this method. The satellite was used SPOT 1 in 1986.
Finally, there is the cadastre direct. This method has been used for over a hundred years and data collected by this method is still used in digital elevation models today, including the mountainous regions that are difficult to map precise using remote sensing techniques.
Current Uses
The digital elevation maps are now used in a variety of areas. Among these are services and GPS location of consumers in other basic services, flight simulators, land evaluation, precision agriculture, transportation systems and intelligent systems developed to support driver.
Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire